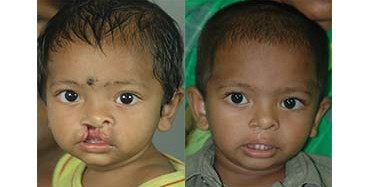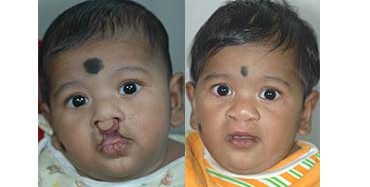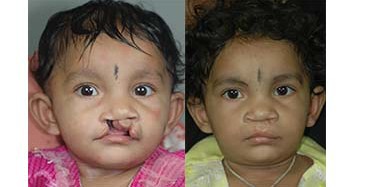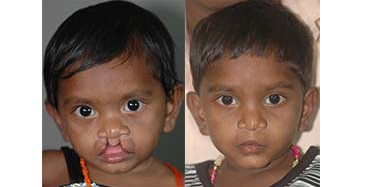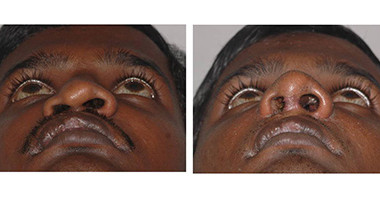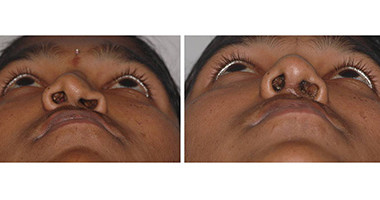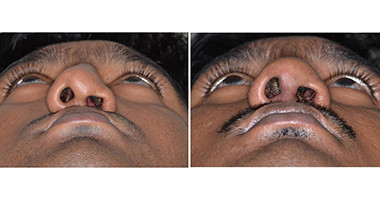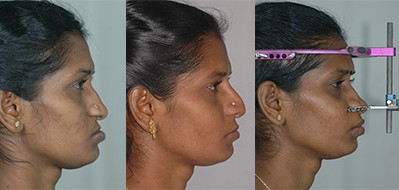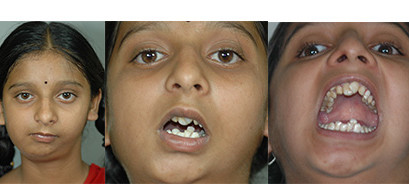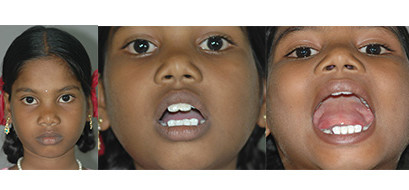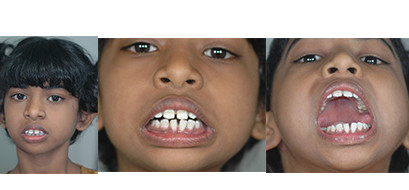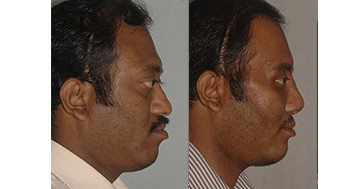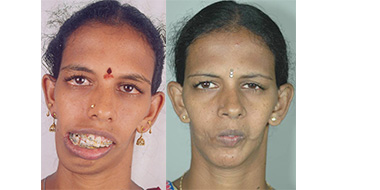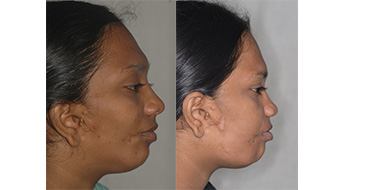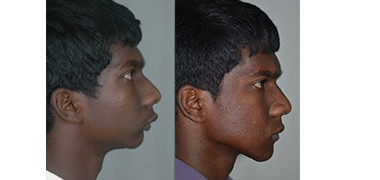
Cleft Lip
Around 3 months after birth, the first surgery is performed to close the cleft lip. The preferred age is at approximately 10 weeks, following “Rule of 10” (the child is at least 10 weeks of age, weighs at least 10 pounds(5 kgs),and has at least 10 grams% of haemoglobin).If the cleft is bilateral and extensive, the child may require small corrective surgeries of lip at a later stage.
Cleft Palate & Speech Management
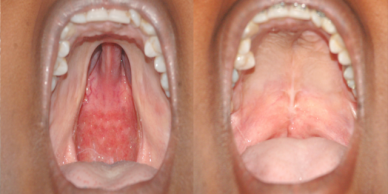
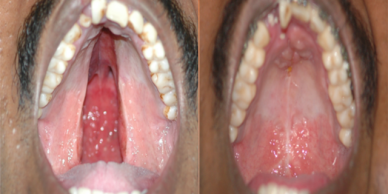
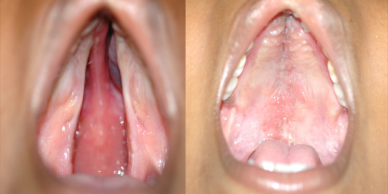
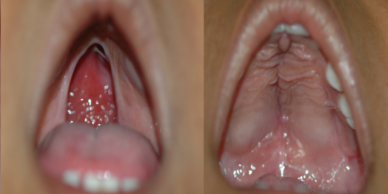
Cleft palate is corrected by surgery usually performed between 9 to 12 months. Approximately 20-25% require only one palatal surgery to achieve good seal in the throat, capable of producing normal speech. However combination of surgery and rigorous speech therapy helps in achieving better speech.
Additional corrective surgeries in throat and palate to correct the speech are best done before 5-7 Years of age, as this is the age at which speech pattern function of the palatal muscles gets imprinted in the Brain.
Cleft Alveolus (Bone defect in upper jaw)
The cleft extends into the upper jaw creates gap[bony defect]. The gap is usually corrected by filling the defect with bone. The bone can be taken from the patients own body, usually hip. This procedure is called Bone grafting and is performed at an age of 8-9 years. This helps in tooth eruption, jaw development and orthodontic treatment.
Jaws & Growth
Operated Cleft lip and palate patients can have growth disturbances in upper jaw with abnormal teeth eruption. These patients will need special Orthodontic Treatment.
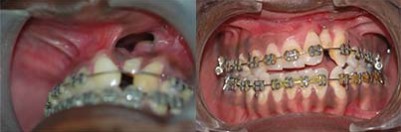
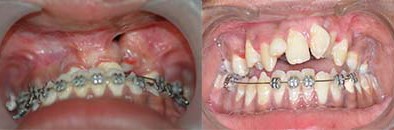
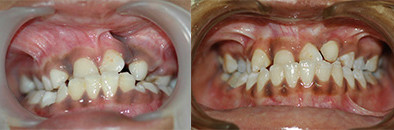
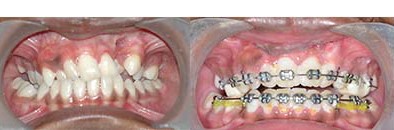
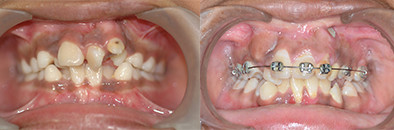
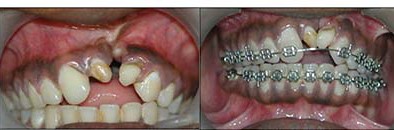
Orthodontic Alignment: (Braces on teeth)
This process involves alignment of teeth in the jaws. This will improve the patients smile and augments the aesthetic outcome of the patient. This can be started once the permanent teeth erupt, that is any time after 8 years of age. It also improves speech by correcting articulation.
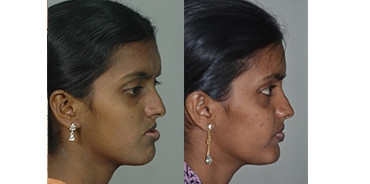
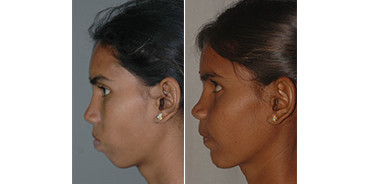
Orthognathic Surgery (Corrective Jaw operation)
Surgery may be needed to correct the position of the jaws and facilitate the patient to chew and bite. This can be performed when the patients are above 17 years of age.
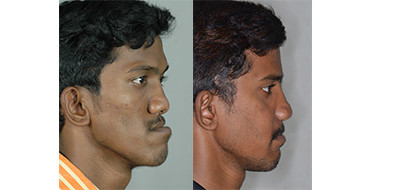
Rhinoplasty (Nose Correction)
Cleft lip patients can have deformities of the nose and difficulty in breathing through one side of the nose. Nose surgery is performed after the correction of the jaws (after 18 yrs) that form the foundation for the position of the nose. This operation not only improves appearance but also improves breathing.
Distraction Osteogenesis
Distraction Osteogenesis is an advanced surgical procedure that involves stretching the callus that forms during the process of bone healing.
This procedure ensures better stability compared to conventional Orthognathic procedures especially when extensive amount of jaw movements are necessary in all the three dimensions.
Temporo Mandibular Joint Ankylosis
TMJ ankylosis means fusion of the jaw joint that leads to difficulty in mouth opening.
This is commonly seen in children secondary to facial injury (after a fall) and middle ear infections.
This can also lead to aesthetic deformity along with breathing difficulty and snoring which needs surgical release of the joint at the earliest followed by aesthetic correction of the jaws by bone lengthening.
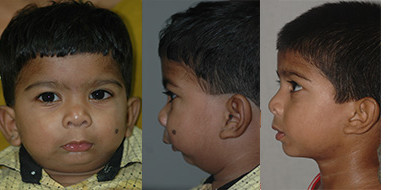
Crouzons Syndrome
This is caused because of the early fusion of the growth centres in the skull (bones covering brain) of the child.
This leads to deficient growth of the mid part of the face with protrusion of the eye balls, breathing difficulties , snoring and unesthetic appearance. This is corrected by the surgery of the skull that will facilitate the growth of the brain followed by the surgery of the mid part of the face . This will also protect eyeball from injury.
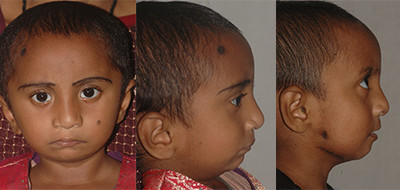
Hemifacial Microsomia (Defective growth of one side of face)
This is the condition in which one half of the face fails to grow. This may be associated with malformed ears, malformed lower jaw, facial nerve palsy, and macrostomia ( large mouth due to cleft on the side of the lips).
This is caused because of the bleeding into the fetus during its growth in the mother’s womb.
These patients need multiple surgical procedures including mandibular distraction (Procedures to lengthen the jaws), ear reconstruction, orthodontic treatment and bone grafting.
Pierrie Robin Sequence
This is characterised by presence of extremely small lower jaw with cleft of palate.
This can lead to severe breathing and feeding difficulties after child birth needing emergency treatment.
This can be treated by Neonatal/ Pediatric mandibular bone lengthening followed by correction of cleft palate.
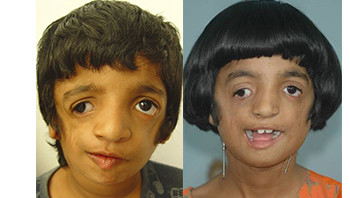
Treacher Collins Syndrome
This is a genetic anomaly that leads to deformity of the complete middle part of face and the lower jaw along with deformity of the ears on both sides.
These patients need staged treatment by bone lengthening, ear reconstruction and mid face correction (entire jaw correction).
Speech Therapy
Normally cleft Lip/palate patients will have speech problems,particularly Hypernasality and misarticulation.These can be corrected if speech therapy is given at appropriate age (from 3 to 6 years).
Treatment schedule
| 0 m |
3 m |
6 m |
9 m |
1 y |
2 y |
3 y |
4 y |
5 y |
6 y |
7 y |
8 y |
9 y |
10 y |
11 y |
12 y |
13 y |
14 y |
15 y |
16 y |
17 y |
18 y |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Palatal plate |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Cleft Lip surgery |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Cleft palate surgery |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Ear tube placement |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Speech therapy,
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Bone grafting of the jaw |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Orthodontics(clip treatment) |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Further cosmetic corrections
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Rhinoplasty(nose correction) |